What is the role of tonsils and adenoids ?
Tonsils and adenoids are organs of the lymphoid system, which is one of the body's defense mechanisms.
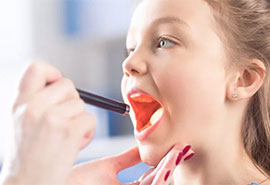
Are the tonsils and adenoids visible when the mouth is open ?
The tonsil is seen when the patient opens his mouth during the examination, but the adenoid is located in the area where the nose opens backwards, behind the soft palate and cannot be seen in this way.
How can the adenoids be seen ?
The adenoid can be seen through cameras using instruments called endoscopes. However, it may not always be possible to perform this examination in children. In this case, if necessary, an evaluation can be made on the projection of the adenoid by taking an X-ray.
They said my child has adenoids. What does it mean ?
Actually, this is an incorrect definition. Because adenoids are present in every child. The correct expression should be 'large adenoids'. Normally, the adenoids grow up to 5 years old and starts to regress after 5 years of age. However, this regression does not occur in every child.
What problems can large adenoids cause ?
When the adenoids are large, it can create a blockage at the point where the nose opens backwards. In this case, the child may have nasal obstruction, sleep with mouth open, snoring, and apnea especially if the tonsils are also enlarged. If this is not noticed and intervened in the right time, the development of the child's face and palate may be affected. Nasal breathing is very important during childhood. A child who constantly breathes through his or her mouth and snores, may have low nasal bridge, high palate, and protruding teeth, which may change his or her expression, leading to ‘adenoid face’.
How else can apnea due to large tonsils and adenoids harm my child ?
Sleep quality is very important for children. Some hormones released during sleep play an important role in the healthy growth of the child. Studies have shown that these substances decrease in children with poor sleep quality and apnea, and that these substances increase after tonsil and adenoid surgery.
What other harms do adenoids cause ?
Adenoids serve as a reservoir for some microbes. For this reason, adenoids play an important role both in chronic nasal discharge, bad breath and sinusitis in children, as well as in middle ear infections and effusion in the ear.
How can microbes in the adenoid affect the middle ear ?
The middle ear is connected to the nasal cavity via the Eustachian tube. The main function of the Eustachian tube is to provide ventilation and drainage of the middle ear. The orifice of the Eustachian tube, which is normally closed, opens with swallowing and yawning. In children, the Eustachian tube runs more horizontally in the head. It reaches its adult angle at the age of 7. This makes it easier for the microbes in the nasal cavity to reach the middle ear during childhood.
What is the most common cause of tonsillitis ?
Viruses are the most common cause of tonsillitis. Bacteria cause tonsillitis to a lesser extent than viruses.
How can you tell if tonsillitis is caused by viruses or bacteria ?
Your doctor can make a clinical distinction between viral and bacterial infection based on some findings such as the appearance of the tonsils, the condition of lymph nodes in the neck, the presence of high fever or an accompanying disease such as common cold, flu, and blood tests results. A throat swab test, called the rapid strep test, can be helpful, yet sometimes misleading. Definitive distinction is possible with throat culture.
What is a beta microbe ?
The microbe, which is briefly expressed as beta microbe, and also called as group A beta hemolytic streptococcus in medical language, is the most common cause of bacterial tonsillitis.
If my child has tonsillitis with beta microbe, can it cause a heart or kidney disease ?
These are complications that occur with beta microbes and can be seen in untreated children, related to inflammation of the heart valve and kidney with a reaction of the immune system. Even if they have never been treated, these odds are not high. Moreover, this possibility disappears when antibiotic treatment is started within 10 days of the onset of infection. Today, medical care is better than in the past, and such complications have become even rarer.
When should my child's tonsils be removed ?
The two main reasons for performing tonsil surgery are obstruction and infection. Enlarged tonsils may cause snoring and apnea. Recurrent tonsillitis is defined as bacterial tonsil infection 7 times in a year, or 5 times in 2 consecutive years, or 3 times in 3 consecutive years. Removal of the tonsils is considered in case of recurrent tonsillitis. Currently, we perform tonsillectomy because of the obstruction rather than recurrent infections.
When should my child's adenoids be removed ?
As with tonsils, the main reasons for performing adenoid surgery is the presence of large adenoids that cause obstruction in the child, which cause sleeping with mouth open, snoring or apnea, and infections. These infections are mainly recurrent otitis media, persistent otitis media with effusion, chronic otitis with a permanent perforation in the eardrum, and chronic sinusitis.
If my child's adenoids-tonsils are removed, will he or she is going to be immunocompromised? Will microbes reach lungs directly ?
This is a question that physicians frequently encounter. Such a concern may arise especially when adenoid surgery is scheduled together with tonsillectomy. It is true that the tonsils and adenoids are organs making part of the immune system. However, in a healthy child who does not have a special immune deficiency, removal of tonsils and adenoids do not cause any problem concerning the immune system. There is no scientific data on the increase in lung infections after adenotonsillectomy.
Is the operation performed under general anesthesia ?
These surgeries have also been performed under local anaesthesia in the past. However, it has been observed that operations performed in this way create psychological traumas in children. In my residency, I performed a few adult tonsillectomy under local anaesthesia, yet for years I have been performing these operations only under general anaesthesia.
Is an external incision made in these surgeries ?
No, these surgeries are performed intraorally using special instruments.
Is there an age limit for these surgeries ?
In the past, some age limits were mentioned, especially due to the risks of anaesthesia. There is no such age limit today. However, a very young child is operated only because of apnea. My youngest patient was a 1-year-old boy.
Can tonsil surgery be done without bleeding ?
Today, tonsil surgery with instruments such as bipolar cautery, thermal welding and plasma has become much less bloody compared to the former techniques.
Does it recur when tonsils and adenoids are removed ?
When total tonsillectomy is performed, it does not recur in case the tonsils are properly removed. On the other hand, adenoids might recur, especially when adenoidectomy is performed under the age of three. This probability decreases with age.
Are there differences in tonsil surgery in adults ?
We rarely perform tonsil surgery due to infection in adult patients. The main reason is the large tonsils that cause snoring and apnea during sleep, and when necessary, it is performed together with soft palate and base of the tongue surgeries. Another reason for tonsillectomy, which may occur rarely in adults, is the constant bad breathe related to tonsilloliths. We advise our smoker patients who will undergo tonsillectomy to quit smoking, otherwise they can develop chronic pharyngitis. Apart from this, tonsil surgery is a painful operation and we observe that the post-operative period in adults is more difficult than in children. Especially when it is performed together with soft palate surgeries, the pain increases, and painkillers in the form of injection may be required. The pain usually resolves within 7-10 days.
What should be considered before and after the operation ?
Aspirin should not be taken starting from at least one week before surgery. Again, if adult patients use some medications such as coumadin, they should be discontinued at the appropriate time. The patient should not have any infection, especially tonsillitis, during the operation. After the operation, the patient is given ice cream as it will help reduce oedema and pain. In addition, a diet list containing smooth foods is applied for 1 week to 10 days. Again, painkillers prescribed by the physician should be used after the surgery, and aspirin should not be taken for at least 2 weeks.